We are given a list of (axis-aligned)
rectangles. Each rectangle[i] = [x1, y1, x2, y2] , where (x1, y1) are the coordinates of the bottom-left corner, and (x2, y2) are the coordinates of the top-right corner of the ith rectangle.
Find the total area covered by all
rectangles in the plane. Since the answer may be too large, return it modulo 10^9 + 7.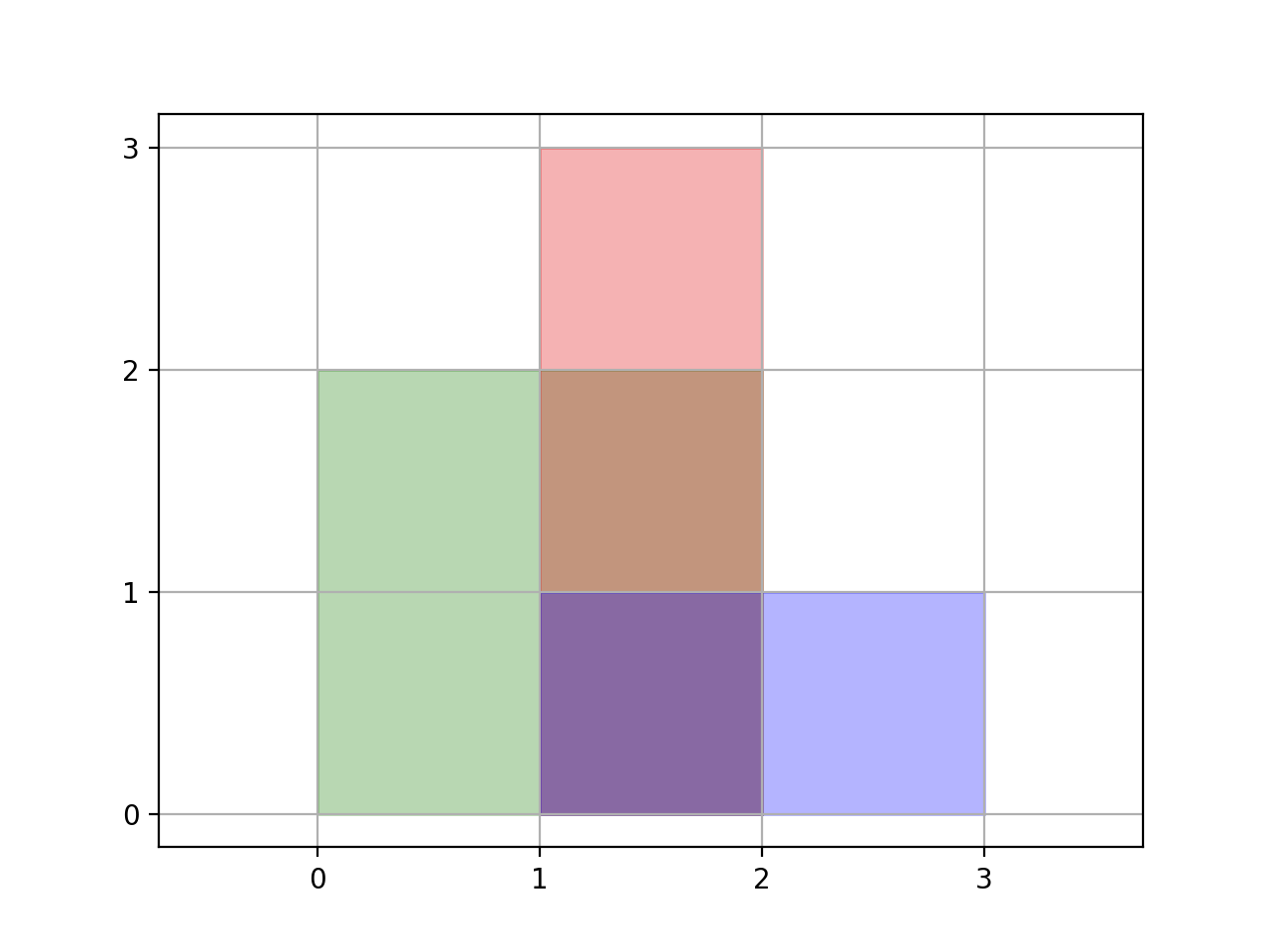
Example 1:
Input: [[0,0,2,2],[1,0,2,3],[1,0,3,1]] Output: 6 Explanation: As illustrated in the picture.
Example 2:
Input: [[0,0,1000000000,1000000000]] Output: 49 Explanation: The answer is 10^18 modulo (10^9 + 7), which is (10^9)^2 = (-7)^2 = 49.
Note:
1 <= rectangles.length <= 200rectanges[i].length = 40 <= rectangles[i][j] <= 10^9- The total area covered by all rectangles will never exceed
2^63 - 1and thus will fit in a 64-bit signed integer.
先按x坐标扫描,每次计算[x1,x2]上的面积大小。一共计算2 * n次
计算过程是对所有在[x1, x2]内的图形进行切割,剩下的塞回去。然后再对y轴进行排列,然后求和。
O(n * n * lg n) time
想法: 如果排序的时候考虑到y轴,那可以去掉第2步的排序,并且把切割完的图形不塞回priority queue里,这样可以优化到O(n * n)
class Solution {
public int rectangleArea(int[][] rectangles) {
PriorityQueue<int[]> que = new PriorityQueue<>((a, b) -> a[0] - b[0]);
for (int[] rec : rectangles) que.add(rec);
long sum = 0;
while (!que.isEmpty()) {
List<int[]> batch = new ArrayList<>();
int[] cur = que.poll();
batch.add(cur);
while (!que.isEmpty() && que.peek()[0] == cur[0]) {
batch.add(que.poll());
}
verticalCut(batch, que);
sum += (long)getSum(batch) * (batch.get(0)[2] - batch.get(0)[0]);
}
return (int)(sum % (1000000000 + 7));
}
private int getSum(List<int[]> batch) {
Collections.sort(batch, (a, b) -> a[1] - b[1]);
List<int[]> temp = new ArrayList<>();
temp.add(batch.get(0));
int i = 1;
while (i < batch.size()) {
int[] cur = batch.get(i);
int[] end = temp.get(temp.size() - 1);
if (cur[1] <= end[3]) {
end[3] = Math.max(end[3], cur[3]);
}else {
temp.add(cur);
}
i++;
}
int sum = 0;
for (int[] t : temp) {
sum += t[3] - t[1];
}
return sum;
}
private void verticalCut(List<int[]> batch, PriorityQueue<int[]> que) {
int min = que.isEmpty() ? batch.get(0)[2] : que.peek()[0];
for (int[] rec : batch) {
min = Math.min(min, rec[2]);
}
for (int[] rec : batch) {
if (rec[2] > min) {
int[] right = new int[]{min, rec[1], rec[2], rec[3]};
rec[2] = min;
que.add(right);
}
}
}
}
Solution #2
Ref: https://leetcode.com/problems/rectangle-area-ii/discuss/139835/TopJava-Solution-with-detailed-explaination-check-this-one-!
- 存线段的话还是不能解决当x点时的情况,所以只能存点
- 点的val是为了更方便的计算进出。因为左下是1,所以右下跟左上只能设为-1,从而右上只能设为1
- preY是只计算矩形左边的边
- getY里的count是为了计算当前进出
- 用ide跑几个test case就能明白代码
O(n^2)
class Solution {
class Point {
public int x;
public int y;
public int val;
public Point(int x, int y, int val) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
this.val = val;
}
}
public int rectangleArea(int[][] rectangles) {
List<Point> points = new ArrayList<>();
for (int[] r : rectangles) {
int x1 = r[0], x2 = r[2],y1 = r[1], y2 = r[3];
points.add(new Point(x1,y1, 1));
points.add(new Point(x1,y2, -1));
points.add(new Point(x2,y1, -1));
points.add(new Point(x2,y2, 1));
}
Collections.sort(points, (a, b) -> {
return a.x - b.x;
});
Map<Integer, Integer> map = new TreeMap<>();
int preX = -1, preY = -1;
int rt = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < points.size(); i++) {
Point p = points.get(i);
map.put(p.y, map.getOrDefault(p.y, 0) + p.val);
if (i == points.size() - 1 || points.get(i + 1).x > p.x) {
if (preX > -1) {
rt += ((long)preY * (p.x - preX)) % (1000000007);
rt %= (1000000007);
}
preY = getY(map);
preX = p.x;
}
}
return rt;
}
private int getY(Map<Integer, Integer> map) {
int rt = 0, preY = -1, count = 0;
for (Map.Entry<Integer, Integer> entry : map.entrySet()) {
if (preY != -1 && count > 0) {
rt += entry.getKey() - preY;
}
count += entry.getValue();
preY = entry.getKey();
}
return rt;
}
}
Solution #3, Segment Tree O(n * lg n)
Ref: https://leetcode.com/problems/rectangle-area-ii/solution/
No comments:
Post a Comment