You are given a doubly linked list which in addition to the next and previous pointers, it could have a child pointer, which may or may not point to a separate doubly linked list. These child lists may have one or more children of their own, and so on, to produce a multilevel data structure, as shown in the example below.
Flatten the list so that all the nodes appear in a single-level, doubly linked list. You are given the head of the first level of the list.
Example:
Input: 1---2---3---4---5---6--NULL | 7---8---9---10--NULL | 11--12--NULL Output: 1-2-3-7-8-11-12-9-10-4-5-6-NULL
Explanation for the above example:
Given the following multilevel doubly linked list:
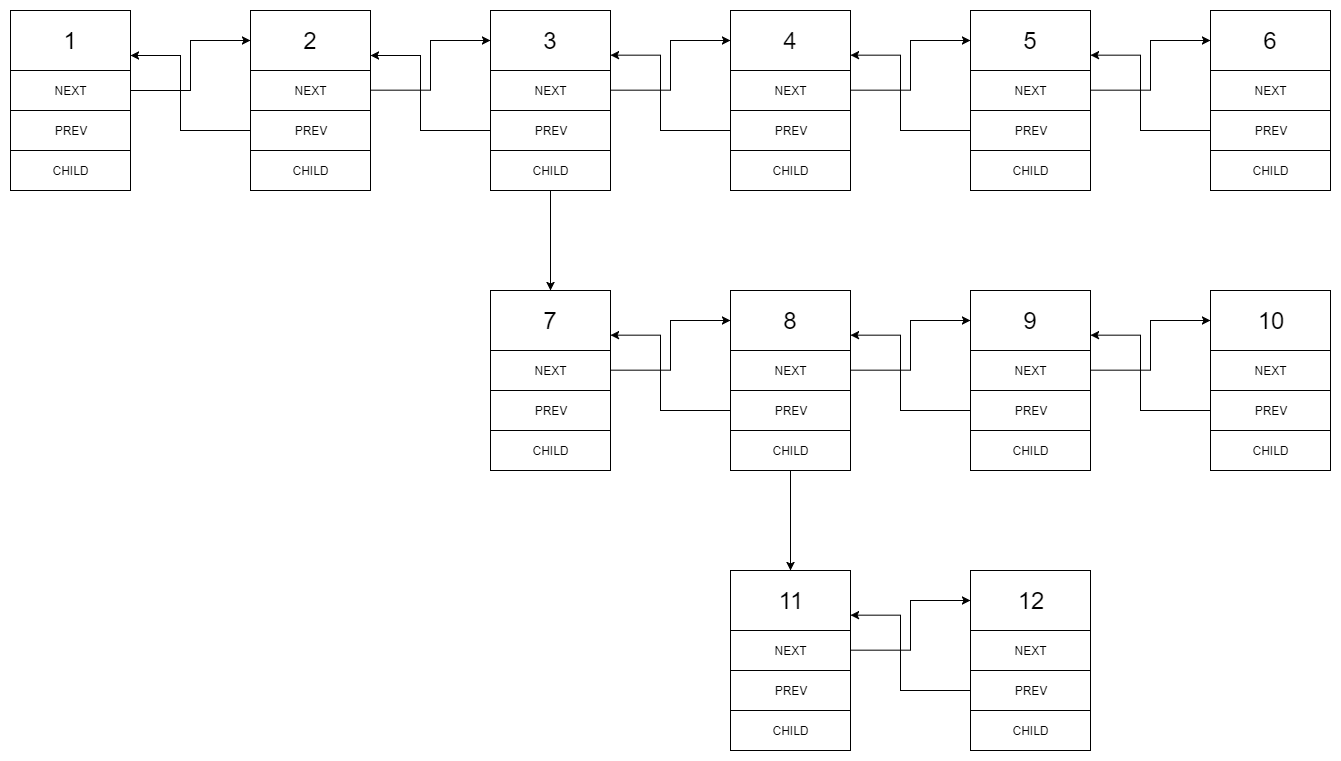
We should return the following flattened doubly linked list:

Solution #1, recursive
/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
public int val;
public Node prev;
public Node next;
public Node child;
public Node() {}
public Node(int _val,Node _prev,Node _next,Node _child) {
val = _val;
prev = _prev;
next = _next;
child = _child;
}
};
*/
class Solution {
public Node flatten(Node head) {
if (head == null) return null;
Node cp = head;
rec(cp);
return head;
}
private Node rec(Node head) {
if (head.next == null && head.child == null) return head;
if (head.child == null) {
return rec(head.next);
}
Node savedNext = head.next;
head.next = head.child;
head.child.prev = head;
Node last = rec(head.child);
head.child = null;
last.next = savedNext;
if (savedNext != null) {
savedNext.prev = last;
}
savedNext = last;
return rec(savedNext);
}
}
Solution #2, iterative. 如果有child,就把child整个list并回主list(暂时先放过child的child),然后再从child开始走。每次都减少一层
O(n), 因为每个node最多被走了2次
/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
public int val;
public Node prev;
public Node next;
public Node child;
public Node() {}
public Node(int _val,Node _prev,Node _next,Node _child) {
val = _val;
prev = _prev;
next = _next;
child = _child;
}
};
*/
class Solution {
public Node flatten(Node head) {
Node itr = head;
while (itr != null) {
if (itr.child != null) {
Node savedNext = itr.next;
itr.next = itr.child;
itr.child.prev = itr;
itr.child = null;
Node itrInner = itr.next;
while (itrInner.next != null) {
itrInner = itrInner.next;
}
itrInner.next = savedNext;
if (savedNext != null) savedNext.prev = itrInner;
}
itr = itr.next;
}
return head;
}
}
No comments:
Post a Comment